ZF
Basic structure of the ZFN
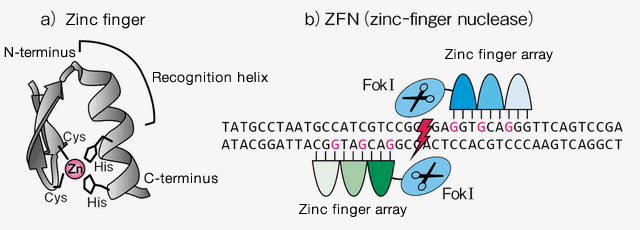
- The C2H2 zinc finger motifs, which are used to engineer ZFNs, consist of two β sheets and one α helix. The recognition helices bind to specific base sequences.
- ZFNs are artificial restriction enzymes that consist of one or more zinc-finger DNA-binding domains fused to a non-specific FokⅠ endonuclease domain. A series of zinc-finger DNA-binding domains is called a zinc-finger array. ZFNs are used in pairs that target sites on opposite DNA strands. The FokⅠ catalytic domains dimerize to create a double-strand break (DSB).
Adapted from: T. Yamamoto. Basic Principles and Application of Genome Editing (in Japanese). Tokyo, Japan: Shokabo; 2018.